Evaluation of RAG pipelines with Ragas
Langfuse offers the feature to score your traces and spans. They can be used in multiple ways across Langfuse:
- Displayed on trace to provide a quick overview
- Segment all execution traces by scores to e.g. find all traces with a low-quality score
- Analytics: Detailed score reporting with drill downs into use cases and user segments
Ragas is an open-source tool that can help you run Model-Based Evaluation on your traces/spans, especially for RAG pipelines. Ragas can perform reference-free evaluations of various aspects of your RAG pipeline. Because it is reference-free you don’t need ground-truths when running the evaluations and can run it on production traces that you’ve collected with Langfuse.
The Environment
import os
# get keys for your project from https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = ""
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = ""
# your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ""
# Your host, defaults to https://cloud.langfuse.com
# For US data region, set to "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com"
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "http://localhost:3000"%pip install langfuse datasets ragas llama_index python-dotenv openai --upgradeThe Data
For this example, we are going to use a dataset that has already been prepared by querying a RAG system and gathering its outputs. See below for instruction on how to fetch your production data from Langfuse.
The dataset contains the following columns
question: list[str] - These are the questions your RAG pipeline will be evaluated on.answer: list[str] - The answer generated from the RAG pipeline and given to the user.contexts: list[list[str]] - The contexts which were passed into the LLM to answer the question.ground_truths: list[list[str]] - The ground truth answer to the questions. However, this can be ignored for online evaluations since we will not have access to ground-truth data in our case.
from datasets import load_dataset
fiqa_eval = load_dataset("explodinggradients/fiqa", "ragas_eval")['baseline']
fiqa_evalThe Metrics
For going to measure the following aspects of a RAG system. These metric are from the Ragas library:
- faithfulness: This measures the factual consistency of the generated answer against the given context.
- answer_relevancy: Answer Relevancy, focuses on assessing how pertinent the generated answer is to the given prompt.
- context precision: Context Precision is a metric that evaluates whether all of the ground-truth relevant items present in the contexts are ranked high. Ideally all the relevant chunks must appear at the top ranks. This metric is computed using the question and the contexts, with values ranging between 0 and 1, where higher scores indicate better precision.
- aspect_critique: This is designed to assess submissions based on predefined aspects such as harmlessness and correctness. Additionally, users have the flexibility to define their own aspects for evaluating submissions according to their specific criteria.
Checkout the RAGAS documentation to know more about these metrics and how they work.
# import metrics
from ragas.metrics import faithfulness, answer_relevancy, context_precision
from ragas.metrics.critique import harmfulness
# metrics you chose
metrics = [faithfulness, answer_relevancy, context_precision, harmfulness] Now you have to initialize the metrics with LLMs and Embeddings of your choice. In this example we are going to use OpenAI.
from ragas.run_config import RunConfig
from ragas.metrics.base import MetricWithLLM, MetricWithEmbeddings
# util function to init Ragas Metrics
def init_ragas_metrics(metrics, llm, embedding):
for metric in metrics:
if isinstance(metric, MetricWithLLM):
metric.llm = llm
if isinstance(metric, MetricWithEmbeddings):
metric.embeddings = embedding
run_config = RunConfig()
metric.init(run_config)from langchain_openai.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_openai.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
# wrappers
from ragas.llms import LangchainLLMWrapper
from ragas.embeddings import LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper
llm = ChatOpenAI()
emb = OpenAIEmbeddings()
init_ragas_metrics(
metrics,
llm=LangchainLLMWrapper(llm),
embedding=LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper(emb),
)The Setup
You can use model-based evaluation with Ragas in 2 ways
- Score each Trace: This means you will run the evaluations for each trace item. This gives you much better idea since of how each call to your RAG pipelines is performing but can be expensive
- Score as Batch: In this method we will take a random sample of traces on a periodic basis and score them. This brings down cost and gives you a rough estimate the performance of your app but can miss out on important samples.
In this cookbook, we’ll show you how to setup both.
Score with Trace
Lets take a small example of a single trace and see how you can score that with Ragas. First lets load the data
row = fiqa_eval[0]
row['question'], row['answer']Now lets init a Langfuse client SDK to instrument you app.
from langfuse import Langfuse
langfuse = Langfuse()langfuse.auth_check()Here we are defining a utility function to score your trace with the metrics you chose.
async def score_with_ragas(query, chunks, answer):
scores = {}
for m in metrics:
print(f"calculating {m.name}")
scores[m.name] = await m.ascore(
row={"question": query, "contexts": chunks, "answer": answer}
)
return scoresYou compute the score with each request. Below I’ve outlined a dummy application that does the following steps
- gets a question from the user
- fetch context from the database or vector store that can be used to answer the question from the user
- pass the question and the contexts to the LLM to generate the answer
All these step are logged as spans in a single trace in langfuse. You can read more about traces and spans from the langfuse documentation.
# start a new trace when you get a question
question = row['question']
trace = langfuse.trace(name = "rag")
# retrieve the relevant chunks
# chunks = get_similar_chunks(question)
contexts = row['contexts']
# pass it as span
trace.span(
name = "retrieval", input={'question': question}, output={'contexts': contexts}
)
# use llm to generate a answer with the chunks
# answer = get_response_from_llm(question, chunks)
answer = row['answer']
trace.span(
name = "generation", input={'question': question, 'contexts': contexts}, output={'answer': answer}
)
# compute scores for the question, context, answer tuple
ragas_scores = await score_with_ragas(question, contexts, answer)
ragas_scoresOnce the scores are computed you can add them to the trace in Langfuse:
# send the scores
for m in metrics:
trace.score(name=m.name, value=ragas_scores[m.name])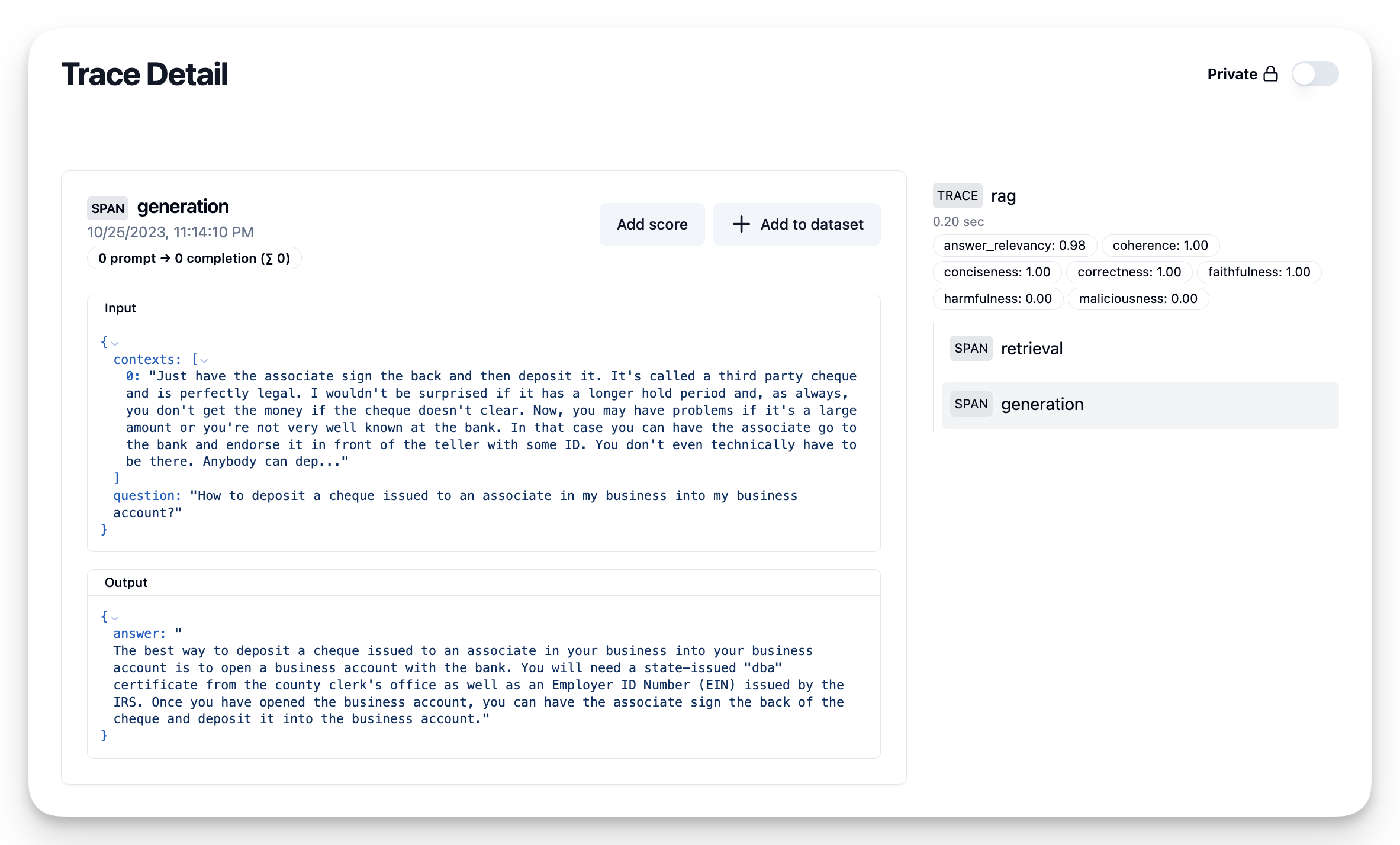
Note that the scoring is blocking so make sure that you sent the generated answer before waiting for the scores to get computed. Alternatively you can run score_with_ragas() in a separate thread and pass in the trace_id to log the scores.
Or you can consider
Scoring as batch
Scoring each production trace can be time-consuming and costly depending on your application architecture and traffic. In that case, it’s better to start off with a batch scoring method. Decide a timespan you want to run the batch process and the number of traces you want to sample from that time slice. Create a dataset and call ragas.evaluate to analyze the result.
You can run this periodically to keep track of how the scores are changing across timeslices and figure out if there are any discrepancies.
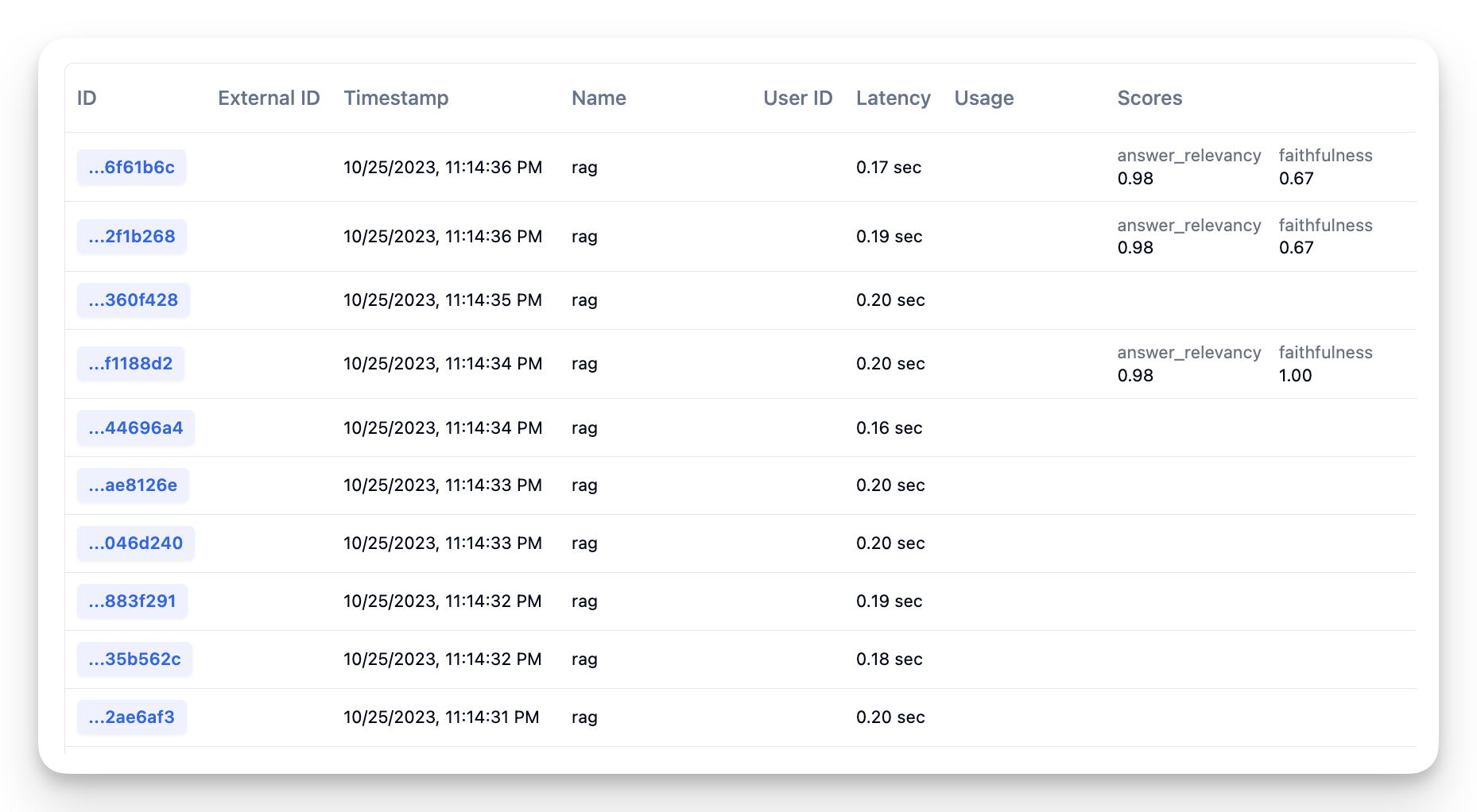
To create demo data in Langfuse, lets first create ~10 traces with the fiqa dataset.
# fiqa traces
for interaction in fiqa_eval.select(range(10, 20)):
trace = langfuse.trace(name = "rag")
trace.span(
name = "retrieval",
input={'question': question},
output={'contexts': contexts}
)
trace.span(
name = "generation",
input={'question': question, 'contexts': contexts},
output={'answer': answer}
)
# await that Langfuse SDK has processed all events before trying to retrieve it in the next step
langfuse.flush()Now that the dataset is uploaded to langfuse you can retrieve it as needed with this handy function.
def get_traces(name=None, limit=None, user_id=None):
all_data = []
page = 1
while True:
response = langfuse.client.trace.list(
name=name, page=page, user_id=user_id
)
if not response.data:
break
page += 1
all_data.extend(response.data)
if len(all_data) > limit:
break
return all_data[:limit]from random import sample
NUM_TRACES_TO_SAMPLE = 3
traces = get_traces(name='rag', limit=5)
traces_sample = sample(traces, NUM_TRACES_TO_SAMPLE)
len(traces_sample)Now lets make a batch and score it. Ragas uses huggingface dataset object to build the dataset and run the evaluation. If you run this on your own production data, use the right keys to extract the question, contexts and answer from the trace
# score on a sample
from random import sample
evaluation_batch = {
"question": [],
"contexts": [],
"answer": [],
"trace_id": [],
}
for t in traces_sample:
observations = [langfuse.client.observations.get(o) for o in t.observations]
for o in observations:
if o.name == 'retrieval':
question = o.input['question']
contexts = o.output['contexts']
if o.name=='generation':
answer = o.output['answer']
evaluation_batch['question'].append(question)
evaluation_batch['contexts'].append(contexts)
evaluation_batch['answer'].append(answer)
evaluation_batch['trace_id'].append(t.id)# run ragas evaluate
from datasets import Dataset
from ragas import evaluate
from ragas.metrics import faithfulness, answer_relevancy
ds = Dataset.from_dict(evaluation_batch)
r = evaluate(ds, metrics=[faithfulness, answer_relevancy])And that is it! You can see the scores over a time period.
rYou can also push the scores back into Langfuse or use the exported pandas dataframe to run further analysis.
df = r.to_pandas()
# add the langfuse trace_id to the result dataframe
df["trace_id"] = ds["trace_id"]
df.head()for _, row in df.iterrows():
for metric_name in ["faithfulness", "answer_relevancy"]:
langfuse.score(
name=metric_name,
value=row[metric_name],
trace_id=row["trace_id"]
)